MVVM in Android
MVVM in Android
MVVM stands for Model-View-ViewModel, which is a pattern widely adopted in MS WPF and Silverlight. In this article, I am going to discuss the implementation of MVVM pattern in Android (Java) with the help of Android-Binding framework.Source code for this article can be obtained here.
MVVM redefined for Android
Model: Model in Android can be data coming from within your application (incl. Shared Preferences), Database (in Cursor, or via other Data Access Object) or externally (via Cursor to other Data Contract)View: all the elements displayed in GUI, that includes android.widget.* family, and your custom views
ViewModel: ViewModel exposes properties and commands for the View, it also serves in data binding between the View and the Model. In Android, most of this job is done in Activity
Implementation
We use a simple calculator as an example. As shown in following figure, the calculator consists of some buttons for input and operations, and a text box to display the result. 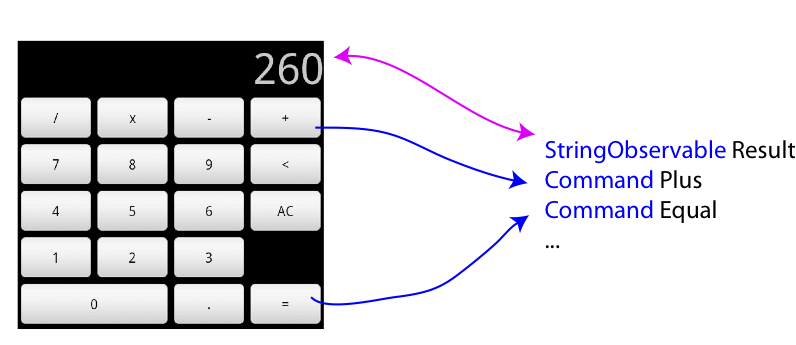
Once we have the ViewModel ready, we need to bind the ViewModel with the View, and here we are using Android-Binding. Android-Binding can help decouple the View with ViewModel, via XML markup of binding syntaxes, all we need to do is include the library, and add an extra namespace in XML markup for Android-Binding to recognize:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:binding="http://www.gueei.com/android-binding/"
android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent">
<TextView android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:textSize="45dip"
android:gravity="right|bottom" binding:text="com.gueei.tutorials.calculator.FormatDisplay(Display)"
android:layout_weight="1"/>
This article will not go deep in how to use Android-Binding, but you may check out following articles and also the source code to know more:
Observable-Command pattern: All properties that the View can bind is wrapped in Observable<T>; while commands implements the Command Interface. This is the primary supported method in Android-Binding
POJO: The ViewModel defines java-styled getter-setter properties, and the ViewModel implements PojoViewModel interface. This is a plugin interface for Android-Binding, and the plugin will convert the ViewModel to Observable-based object.
Here, our example will be in Observable-Command pattern. (POJO version is also available in source code)
Observable<T>
<T> is any Object, while Observable<T> means an property of type T is Observable, whenever changes is made on it, it will notify its subscribers.
So, we have to wrap the above mentioned properties in Observables:
Observable<Double> Result = new Observable<Double>(Double.class, 0d);
Command
Command is similar to public methods of a ViewModel, they can be invoked by UI widgets.
Binding View with ViewModel
Once we implemented the ViewModel, and declared our layout, we need to bind the ViewModel to the View. With a little effort, the binding is done automatically for you with Android-Binding. In the Activity:
Binder.setAndBindContentView(this, R.layout.main, new CalculatorViewModel());
DependentObservable/Converter
Sometimes, we want to format the data, before we present it. For example, we do the calculations using ‘double’ in the calculator, but we don’t want to display the raw double value to user -- the answer can be too verbose for practical usage (like more than 15 significant figure), we want to constraint it to within 10 significant figures.
Of course, we can comb the display value in our ViewModel, before sending it to the View; we do this by using DependentObservable/Converter.
DependentObservable is an Observable that `Observes` other observables, once any of those observables changes, it calculate its value accordingly; a Converter is the same as DependentObservable, only DependentObservable is readonly, an Converter can do reverse conversion.
Since our displayed number in purely for display purpose, we need only DependentObservable. We can explicitly declare the dependentObservable in our ViewModel, but, I would argue that formatting How the view looks like should not be the job of ViewModel, rather, it should be done by View itself.
Android-Binding supports custom Converters (along with some built-in) to declared in XML layout, first, we have to create a class extends from DependentObservable:
public class FormatDisplay extends DependentObservable<CharSequence> {
public FormatDisplay(IObservable<?>[] dependents) {
super(CharSequence.class, dependents);
}
@Override
public CharSequence calculateValue(Object... args) throws Exception {
Double display = (Double)args[0];
DecimalFormat format = new DecimalFormat();
format.applyPattern("#.######");
String output = format.format(display);
if (output.length() <= 10) return output;
format.applyPattern("0.########E00");
return format.format(display);
}
}
Now, we modify our layout to:
<TextView android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:textSize="45dip"
android:gravity="right|bottom"
binding:text="com.gueei.tutorials.calculator.FormatDisplay(Display)"
android:layout_weight="1"/>
In this way, the binding of the Display will become:

Advantages of using MVVM
Just like any other MVVM platform, using MVVM in Android is good for decoupling back end codes from UIs; in the above calculator example, we can plug a different layout to it, without changing anything in the ViewModel (different way to format the display for example).
Other very big advantage of using MVVM, is you can easily do unit test on your ViewModel. You don’t need to really ‘click’ the button to see if the calculation is correct, but just unit-test your ViewModel’s respective Command.
With Android-Binding framework, it generally results much cleaner code. Imagine implementing the event-handler for those 15 buttons in traditional event model, it will end up keeping 15 references to the widget, registering ‘setOnClickListener()’ 15 times, and a massive switch-case-default block for 15 branches of event handling. But with MVVM, the Command interface can describe the purpose of them much clearer.
Final words
I tried to build a few Android MVVM applications, and found out that sometimes the role between ViewModel and Activity can be quite blurry. Since many places in Android Application requires the Context to be used (like getting res, cursor, calling out other activities), it ends up the ViewModel needed to pass the calling Activity to it, or nested the ViewModel in the Activity class, or even Activity class is the ViewModel as well (it’s ok for very simple ViewModel). Such an approach makes ViewModel is working quite parallel with Activity: Activity decided the creation of ViewModel and which View is going to render, also manage the life cycle of ViewModel; ViewModel uses Activity to dispatch requests to outside world.