Doing Arrays - C#
Introduction
An array is a collection of same type variables which can be accessed using
numeric index. The numeric index is written in square brackets after the array
name.
Following is the declaration of single dimension array
int[ ] roll = new int[8];
Characteristics
The numeric index is zero based. It goes from 0 to n-1 where n is size of array
(total number of elements in array).
On declaration, default value of numeric type arrays is set to 0, and reference
type are set to null.
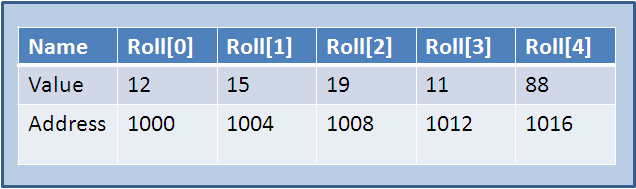
Arrays are stored on continuous memory locations as shown in figure.
In C#, arrays are objects, and they have certain properties like Length, which
can be used by using (.) and property name. All arrays are derived from abstract
class arrays so many built-in methods can be called.
//Rank
propety Return number of dimensions
int[ ] single =
new int[4] { 1,
2, 3, 4 };
int dimension = single.Rank;
Single Dimension Arrays
It is the simplest form of arrays, its kind of a row with n columns where each
column is accessed with the zero based index. The above two codes examples show
single dimension arrays.
In C#, declaration of array is a bit different from c or c++. Here square
brackets are placed after type name, then array-name, keyword new and then type
with square brackets containing size of array.
Type[ ] arrayname = new Type[size];
Following code initializes a single dimension integer array of size 5. It
contains 5 elements which can be accessed by arr[0] to arr[4].
//Integer Array declaration
int[ ] arr
= new int[5];
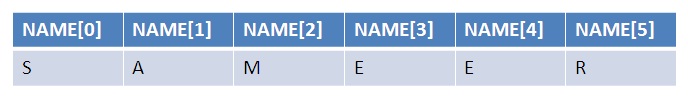
Character type arrays are declared as following
//Character type array
char[ ]
name = new char[10];
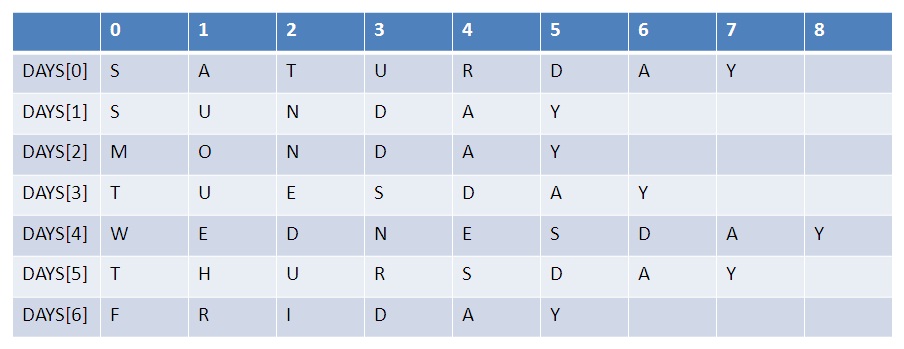
The same way, string type arrays are declared
//String array declaration
string[ ]
days = new string[7];
There are many ways to assign values to array. Array can be initialized in
declaration line by placing the values between curly braces { } in comma
separated fashion. Characters are placed in single quotes and strings are placed
in double quotes.
//Integer Array Initialization
int[ ] arr =
new int[5] { 1,
2, 3, 4, 5 };
//Character Array
Initialization
char[ ] name =
new char[10] {
'i', ' ',
'a', 'm',
' ', 'f',
'i', 'n',
'e', '.'
};
//String Array Initialization
string[ ] days =
new string[7] {
"Sun", "Mon",
"Tue", "Wed",
"Thu", "Fri",
"Sat" };
While initializing the array, size of array may be omitted. Then size of array
will be calculated number of elements written in curly braces.
One other way of declaring, initializing array is
//Integer Array Declaration,
Initialization
int[ ] arr;
arr = new
int[5] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
Following way of assigning values to array will cause Error.
//Wrong way of writing
int[
] arr = new int[5];
arr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
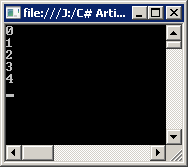
Iterating Through Single Dimension Array
Since in C#, arrays are objects and they retain certain built in properties.
Length property returns total number of elements in array. Right now we are
dealing with single dimension, so total number of elements is equal to size of
array.
for
(int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
Console.ReadLine();
Multi Dimensional Arrays
Arrays can be multidimensional. The most widely used are two dimensional arrays, often Matrices form 2D arrays. In 2D array, 2 zero based index are used to access a particular value in the array.
//Integer 2D Array
int[,] matrix = new int[10, 10];
//Accessing Value
int val = matrix[5, 7];
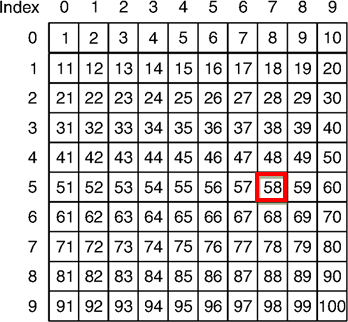
Value of element stored in 5th Row, 7th Column i.e 58, will be assigned to Variable val. Rows and Columns have zero based index. Total number of values which can be stored in 2D array is equal to product of rows and columns. For above case it is 100
Single dimension array is a single Row with columns >0. 2D arrays have more than one Row, thus form a table.
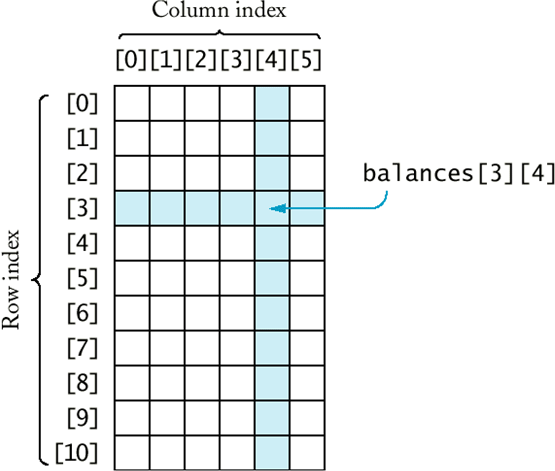
Accessing the element stored in 3rd row, 4th column in balances table.
To initialize 2D array, each row values are placed in curly braces as in case of single dimensional array and then these set of curly braces for all rows are placed in another set of curly braces in same fashion.
//2D Array Initializtion
int[,] arr_2d = new int[3, 2] { { 1, 2 }, { 3, 4 }, { 5, 6 } };
//Initializing 2Dimensional Array
char[,]
day = new char[2,
3] { { 'o', 'n',
'e' }, { 't',
'w', 'o' }
};
In above piece of code, there are 3 rows, 2 columns, thus total number of
elements is 2 x 3 = 6. Its hard to initialize 2D array shown in 1st figure,
where it has 10 rows and 10 columns. Loops can be used to assign values to each
location.
//Assigning Values to matrix[10,10] array
for
(int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
for (int j =
0; j < 10; j++)
{
matrix[i, j] = i * 10 + j + 1;
}
}
In case of multidimensional arrays, knowing number of dimensions is sometimes
necessary to have more grip over the array. Rank property returns number of
dimensions of the array.
//Getting Number of dimensions of array
int
dim = matrix.Rank;
The GetUpperBound function returns the upper bound of the array in a particular
dimension.
for
(int i = 0; i <= matrix.GetUpperBound(0);i++)
{
for (int j =
0; j <= matrix.GetUpperBound(1); j++)
{
Console.Write(matrix[i, j].ToString()
+ "\t");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
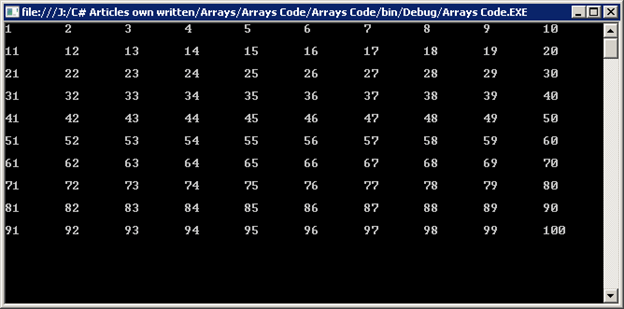
Output of above piece of code.
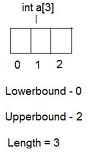
GetLowerBound method gets the lower bound of the array in a particular
dimension. Following figure shows the difference between length, upper bound and
lower bound.
We can have more than two dimensions for arrays as well. For three dimensional
array, we need three index to access each element in array. Example of 3
dimensional array can be a point in space. Consider a block of small bricks, as
shown in figure below, to address each small brick, there is one index for row,
one for column and one for depth.
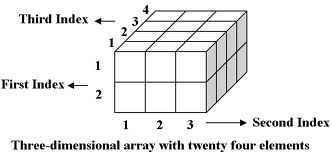
//Block code 3D array
int[, ,]
block_3d = new int[2,
3, 4];
Example of 4 dimensional array can be taken as one second in a week, there are
60 seconds in one hour, 60 mins in one hour, 24 hours a day and 7 day a week.
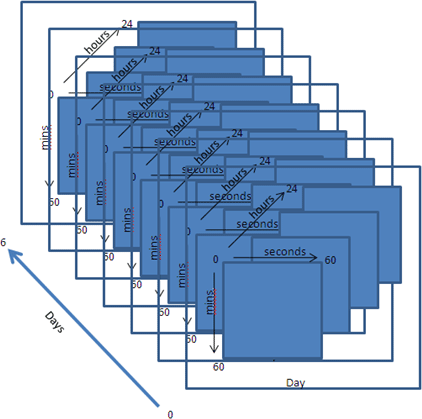
//Week 4D array
int[, , ,]
week = new int[7,
24, 60, 60];

Jagged Arrays
Array of arrays are called jagged arrays.
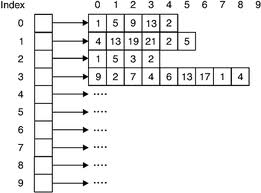
The statement might be confusing but consider the example of saving marks of few
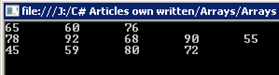
students who are studying different number of subjects.
Student-1 marks 65, 60, 76
Student-2 marks 78, 92, 68, 90, 55
Student-3 marks 45, 59, 88, 72
If we use 2Dimensional array to store the above marks, then an array of 3 rows
and 5 columns is needed. The extra info needs to be added at locations for which
marks don't exist.
|
65 |
60 |
76 |
0 |
0 |
|
78 |
92 |
68 |
90 |
55 |
|
45 |
53 |
88 |
72 |
0 |
Jagged arrays come handy in such situation. Jagged
Arrays may have different sizes and dimensions. For this situation, we need one
single dimension array with three elements, and each of its elements is a single
dimension array with length 3, 5, 4 respectively.
//Jagged arrays
int[ ][ ]
student = new int[3][
];
In above piece of code, two sets of square brackets are used. Now each element
of Jagged array needs to be assigned to a single dimension array.
//Declaring Each Element of Jagged
Array
student[0] = new
int[3];
student[1] = new int[5];
student[2] = new int[4];
Values can also be assigned just like single dimension array by placing after
square brackets.
//Initializing Each Element of Jagged Array
student[0] = new int[3]
{ 65, 60, 76 };
student[1] = new int[5]
{ 78, 92, 68, 90, 55 };
student[2] = new
int[4] { 45, 59, 88, 72 };
A short way of doing this is
//Jagged arrays
int[
][ ] student = new int[3][
]
{
new
int[3] { 65, 60, 76 },
new
int[5] { 78, 92, 68, 90, 55 },
new
int[4] { 45, 59, 88, 72 }
};
Jagged arrays are reference type, thus they are initialized to null. To access
elements in jagged array in student example, 2 indexes are used.
//Accessing elements in Jagged Array
student[2][2] = 80;
for
(int i = 0; i < student.Length; i++)
{
for (int j =
0; j < student[i].Length; j++)
{
Console.Write(student[i][j]);
Console.Write('\t');
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
Mixed Arrays
Combination of jagged and multidimensional arrays is known as mixed arrays. In
case of multidimensional arrays of different sizes, mixed arrays are used.
Consider there are three tables, each with different number or rows and columns.
Table-1 3 rows, 5 columns
Table-2 4 rows, 3 columns
Table-2 6 rows, 4 columns
//Mixed
Arrays
int [ ][,]mixed=new
int[3][ ]
{
new int[3,5],
new int[4,3],
new int[6,4]
};
Have Nice Time.
Do suggest, comment and vote to keep it alive.
*Suggested Changes Incorporated.